Properly managing stormwater runoff is not just an environmental responsibility—it’s a legal requirement for construction and landscaping projects. At A Better Edge, we understand the importance of complying with Stormwater Pollution Prevention Plan (SWPPP) requirements while creating beautiful, functional landscapes for our Colorado customers.
Understanding SIP Requirements in Colorado
SWPPP requirements serve as the foundation for effective stormwater management on construction sites. These requirements are particularly crucial in Colorado due to our unique climate and topography. When heavy rain falls on our mountainous terrain, the potential for erosion and water pollution increases significantly.
The Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment (CDPHE) enforces SWPPP requirements under the National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) program. Any construction activity that disturbs one acre or more requires a stormwater permit and an implemented SWPPP.
When is a SWPPP Required in Colorado?
The following table outlines when a SWPPP is required for Colorado construction projects:
| Project Characteristic | SWPPP Required? | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Disturbing ≥ 1 acre of land | Yes | Includes total project area, even if construction occurs in phases |
| Disturbing < 1 acre but part of a larger standard plan | Yes | “Common plan” refers to construction activities in a larger project. |
| Sites discharging to state waters | Yes | Includes streams, lakes, rivers, and stormwater systems connected to these waters |
| Projects in designated MS4 areas | Yes | Municipal Separate Storm Sewer System areas have additional requirements |
| Residential projects < 1 acre | Generally No | Unless part of a larger development or in a sensitive area |
| Linear utility projects | Varies | Based on the total disturbed area and proximity to waterways |
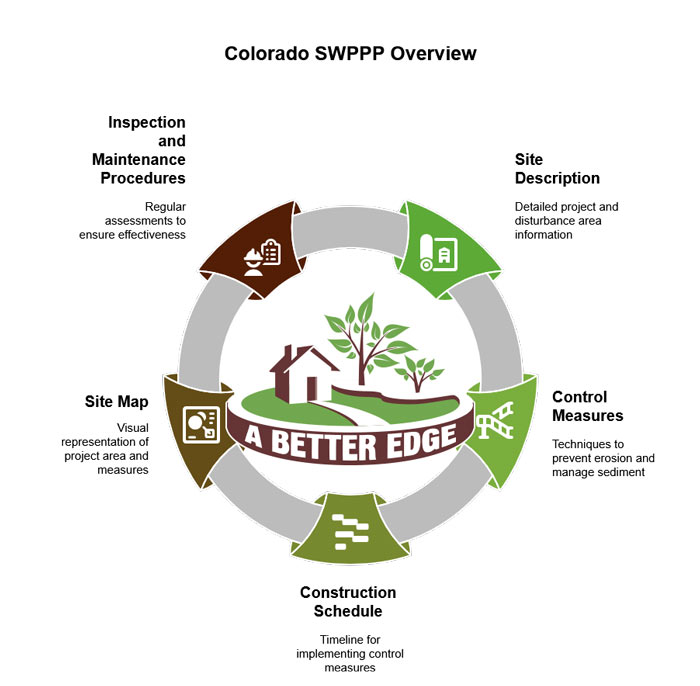
Key Components of SWPPP Requirements
A comprehensive SWPPP must include several essential elements to comply with Colorado regulations. Every SWPPP document should contain:
- Site Description: Detailed information about your project, including the nature of construction activities and the total area of disturbance.
- Control Measures: Specific techniques that will be implemented to prevent erosion and manage sediment.
- Construction Schedule: Timeline for implementing control measures about construction phases.
- Site Map: A visual representation of the project area showing topography, drainage patterns, and the locations of control measures.
- Inspection and Maintenance Procedures: Regular site assessments to ensure control measures remain effective.
At A Better Edge, we help our clients navigate these SWPPP requirements by incorporating effective, attractive solutions that enhance rather than detract from their landscape designs.
SWPPP Document Checklist
| SWPPP Component | Required Content | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Site Description | Project name, location, owner information | Identifies responsible parties |
| Construction activity description | Defines scope of work | |
| The sequence of major activities | Establishes timeline for controls | |
| Estimate of total site area and disturbed area | Determines permit requirements | |
| Site Map | Drainage patterns and slopes | Shows water flow directions |
| Areas of soil disturbance | Identifies vulnerable areas | |
| Location of structural controls | Documents placement of BMPs | |
| Location of stabilization practices | Shows erosion prevention measures | |
| Surface waters and wetlands | Identifies sensitive receptors | |
| Stormwater discharge locations | Shows potential impact points | |
| Control Measures | Erosion control specifications | Prevents soil movement |
| Sediment control details | Captures moving sediment | |
| Materials handling procedures | Prevents chemical contamination | |
| Maintenance Plan | Inspection frequency | Ensures regular monitoring |
| Maintenance protocols | Keeps BMPs functioning properly | |
| Corrective action procedures | Addresses deficiencies | |
| Records | Training documentation | Verifies staff competency |
| Inspection reports | Documents compliance | |
| Spill reports and corrective actions | Tracks incidents and responses |
Sediment Barriers: The First Line of Defense
Among the most critical SWPPP requirements are those related to sediment barriers. These physical structures prevent soil and other pollutants from leaving construction sites during precipitation events.
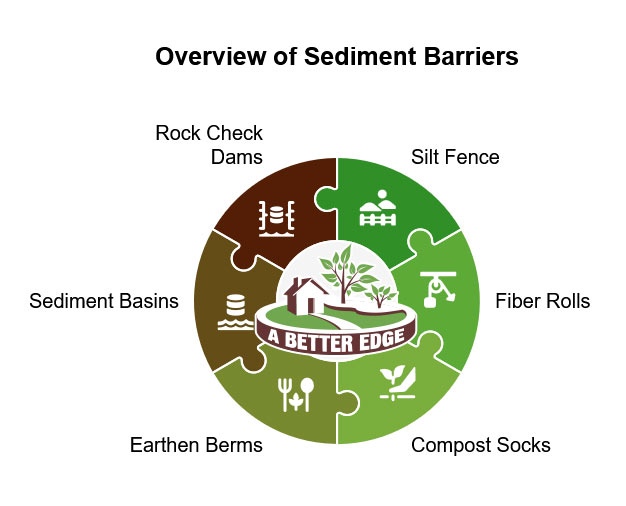
Types of Sediment Barriers
Different projects require different approaches to sediment control. Common types of barriers that satisfy SWPPP requirements include:
Sediment Barrier Comparison
| Barrier Type | Best Applications | Effectiveness | Installation Complexity | Cost | Maintenance Needs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silt Fence | Perimeter control on gentle slopes | Medium-High | Medium | $3-5 per linear foot | High |
| Fiber Rolls | Slope interruption, perimeter control | Medium | Low | $2-4 per linear foot | Medium |
| Compost Socks | Perimeter control, sensitive areas | High | Low | $4-8 per linear foot | Low |
| Earthen Berms | Large areas with available soil | High | Medium | $10-15 per linear foot | Low |
| Sediment Basins | Large sites with concentrated flows | Very High | High | $2,000-5,000+ each | Medium |
| Rock Check Dams | Ditches and swales | High | Medium | $150-300 each | Low |
Silt Fences
Silt fences remain one of the construction sites’ most widely used sediment barriers. They consist of a geotextile fabric supported by wooden or metal stakes, creating a barrier that allows water to pass through while trapping sediment.
For proper installation that meets SWPPP requirements:
- The fabric should be buried in a 6-inch trench to prevent undercutting
- Posts should be spaced no more than 10 feet apart
- The fence should follow the contour of the land rather than crossing slopes
Fiber Rolls/Wattles
These tubular barriers made of compressed plant materials provide excellent sediment control on slopes and along the perimeter of construction sites. They’re particularly effective with other control measures to meet SWPPP requirements.
Berms and Diversions
Earth berms can redirect water away from exposed soils, minimizing erosion and sediment transport. When properly designed and maintained, they provide superior sediment control for projects with significant grading components.
Silt Fence Installation Specifications
Proper installation is crucial for silt fence effectiveness. The following table outlines the specifications required by most Colorado SWPPP requirements:
| Component | Specification | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Filter Fabric | Minimum tensile strength: 120 lbs | Must be woven or nonwoven geotextile |
| Minimum flow rate: 0.3 gal/ft²/min | Allows water passage while trapping sediment | |
| Posts | Minimum length: 4 feet | Must extend at least 18″ above ground |
| Wood posts: minimum 2″×2″ | Must be hardwood | |
| Steel posts: minimum 1.3 lbs/linear ft | Must have projections for fabric attachment | |
| Trench | Minimum depth: 6 inches | Prevents undercutting |
| Minimum width: 4 inches | Allows proper burial of fabric | |
| Post Spacing | Maximum: 6-10 feet | Closer spacing is needed on steep slopes |
| Height | 24-36 inches above ground | Based on the expected water volume |
| Location | Along the same elevation contour | Never up and down slopes |
| Set back 5-10 feet from the toe of the slope | Allows sediment storage |
Stormwater Management Practices
Beyond sediment barriers, SWPPP requirements stipulate a variety of management practices to control stormwater and prevent pollution:
Erosion Control Measures
Preventing erosion at the source is often more effective than capturing sediment later. Effective erosion control measures that satisfy SWPPP requirements include:
Erosion Control Effectiveness by Soil Type
| Control Measure | Sandy Soils | Silty Soils | Clay Soils | Highly Erodible Soils |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temporary Seeding | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| Erosion Control Blankets | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Hydromulch | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ |
| Straw Mulch | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ |
| Surface Roughening | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| Compost Blankets | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Soil Binders | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ |
Rating scale: ⭐ = Minimal effectiveness, ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ = Maximum effectiveness
- Temporary Seeding: Establishing vegetation quickly in disturbed areas
- Erosion Control Blankets: Protecting exposed soil from raindrop impact
- Mulching: Covering bare soil to reduce erosion potential
- Surface Roughening: Creating horizontal ridges in the soil to slow runoff
Inlet Protection
Storm drain inlets must be protected from receiving sediment-laden runoff. SWPPP requirements specify various methods:
- Filter fabric barriers around drain inlets
- Gravel filters around catch basins
- Commercial inlet protection devices
Concrete Washout Areas
Designated areas for removing concrete trucks prevent high-pH concrete wash water from contaminating stormwater. SWPPP requirements mandate that these areas be clearly marked and properly maintained. Learn more about our concrete edging services.
Stabilized Construction Entrances
SWPPP requirements include provisions for preventing mud from tracking onto public roads. Stabilized entrances typically consist of large aggregate (2-3 inch stone) placed over geotextile fabric.
Construction Entrance Specifications
| Specification | Requirement | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Length | Minimum 50 feet | Provides adequate distance for mud removal |
| Width | Minimum 10-12 feet | Accommodates construction vehicles |
| Stone Depth | Minimum 6-8 inches | Ensures durability for heavy traffic |
| Stone Size | 2-3 inch clean stone | Maximizes mud removal from tires |
| Geotextile Underlayment | Required | Prevents mixing of stone with subgrade soil |
| Drainage | Sloped away from the public road | Prevents runoff onto roadway |
| Maintenance | Clean or replace when filled with sediment | Maintains effectiveness |
Implementation Timeline for SWPPP Requirements
In Colorado, SWPPP requirements stipulate specific timelines for implementation:
SWPPP Implementation Schedule
| Phase | Action | Timing | Responsible Party |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Construction | Develop SWPPP document | Before permit application | Owner/Operator |
| Submit NOI and obtain a permit | 30 days before construction | Owner/Operator | |
| Install initial perimeter controls. | Before soil disturbance | Contractor | |
| During Construction | Implement phased BMPs | As specified in the WP | Contractor |
| Conduct regular inspections | Every 14 days & after storms | SWPPP Inspector | |
| Maintain and repair BMPs | Within 7 days of inspection | Contractor | |
| Update SWPPP as needed. | As site conditions change | SWPPP Administrator | |
| Stabilization | Initiate final stabilization | As areas reach the final grade | Contractor |
| Complete stabilization | Within 14 days of final grading | Contractor | |
| Verify 70% vegetation coverage. | Before BMP removal | SWPPP Inspector | |
| Post-Construction | Remove temporary BMPs | After stabilization is established | Contractor |
| Submit NOT | After complete stabilization | Owner/Operator | |
| Retain SWPPP records | Minimum 3 years after NOT | Owner/Operator |
NOI = Notice of Intent, NOT = Notice of Termination, BMP = Best Management Practice
- Before Construction: The SWPPP must be developed, and initial control measures must be installed before ground-disturbing activities begin.
- During Construction: Control measures must be maintained and modified based on regular inspections and changing site conditions.
- After Construction: Temporary control measures can be removed only after stabilizing the site with vegetation or other permanent surface treatments.
Inspection and Maintenance
Regular inspections are a critical component of SWPPP requirements. In Colorado, inspections must be conducted:
- Every 14 days during active construction
- Within 24 hours after any storm event of 0.25 inches or greater
- At the end of snowmelt, if winter conditions prevented regular inspections
SWPPP Inspection Requirements
| Inspection Type | Frequency | Special Conditions | Documentation Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Routine | Every 7-14 days | Based on permit requirements | Complete inspection form |
| Post-Precipitation | Within 24 hours | After ≥0.25″ rainfall or snowmelt | Complete the inspection form with precipitation data |
| Reduced Frequency | Monthly | During winter conditions/site stabilization | Justification in SWPPP |
| Receiving Water | As specified in the permit | For projects discharging to sensitive waters | Special inspection form |
| Winter Conditions | As weather permits | When snow cover prevents inspection | Documentation of conditions |
| Final | Before NOT submittal | Verify complete stabilization | Photographs and final inspection form |
Maintenance activities based on inspection findings might include:
- Removing accumulated sediment from barriers
- Repairing damaged control measures
- Installing additional controls as needed
- Modifying the SWPPP to address changing conditions
Common Challenges with SWPPP Requirements
Meeting SWPPP requirements can present several challenges:
Weather Variability
Colorado’s unpredictable weather patterns can make compliance difficult. Sudden intense storms may overwhelm control measures, while freezing conditions can limit the effectiveness of specific BMPs.
Site Constraints
Urban construction sites with limited space may struggle to implement all necessary control measures. Creative solutions that satisfy SWPPP requirements while minimizing footprint are essential.
Coordination Among Contractors
Multiple contractors working on the same site must coordinate their activities to maintain compliance with SWPPP requirements. Clear communication and shared responsibility are crucial.
SWPPP Challenges and Solutions
| Challenge | Impact | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Limited Space | Difficulty installing traditional BMPs | Use compact alternatives (compost socks instead of silt fence) |
| Employ multi-function BMPs | ||
| Use off-site stormwater management where allowed. | ||
| Extreme Weather | BMP failure during intense storms | Overdesign critical BMPs |
| Implement additional backup measures. | ||
| Develop emergency response procedures. | ||
| Winter Conditions | Frozen ground prevents BMP installation | Install BMPs before freeze |
| Use alternatives designed for cold weather. | ||
| Develop winter-specific SWPPP amendments. | ||
| Multiple Contractors | Coordination difficulties | Designate a single SWPPP coordinator |
| Conduct joint training sessions. | ||
| Implement clear communication protocols. | ||
| Changing Site Conditions | SWPPP becomes outdated | Regular SUP reviews and updates |
| Field adjustment protocols | ||
| As-built documentation process |
Advancing Beyond Minimum SWPPP Requirements
At A Better Edge, we believe in exceeding minimum SWPPP requirements to create genuinely sustainable landscapes. Some advanced approaches include:
Low Impact Development (LID)
LID techniques like rain gardens, bioswales, and permeable pavement go beyond basic SWPPP requirements by mimicking natural hydrologic processes.
Green Infrastructure
Incorporating green infrastructure elements into landscape designs can provide long-term stormwater management solutions that complement temporary SWPPP controls.
Native Landscaping
Using native plants in permanent stabilization satisfies SWPPP requirements, reduces long-term irrigation needs, and enhances habitat value.
Beyond Compliance: Advanced Stormwater Management Approaches
| Approach | Benefits | Integration with SAP | Long-term Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Permeable Pavement | Reduces runoff volume | Can reduce temporary BMP requirements | Requires specialized maintenance |
| Filters pollutants | Addresses post-construction requirements | 15-20 year lifespan with proper care | |
| Recharges groundwater | |||
| Bioretention Areas | Provides aesthetic value | Can be phased from temporary to permanent | Needs regular plant maintenance |
| Creates habitat | Reduces downstream BMP requirements | Enhances property value | |
| Treats stormwater naturally | |||
| Green Roofs | Reduces building energy costs | Usually not part of the construction, SWPPP | 40+ year lifespan with proper maintenance |
| Extends roof membrane life | Can be part of a permanent stormwater plan | Requires specialized structural design | |
| Reduces urban heat island effect | |||
| Rainwater Harvesting | Reduces potable water usage | It can be used for dust control during construction | Requires ongoing system maintenance |
| Reduces downstream erosion | Reduces runoff management needs | Can provide water during drought | |
| Potential cost savings | |||
| Vegetated Swales | Low maintenance | Can replace temporary sediment traps | Requires periodic vegetation management |
| Conveys and treats runoff | Functions during and after construction | Long-term erosion protection | |
| Creates wildlife corridors |
The Cost of Non-Compliance with SWPPP Requirements
Failing to meet SWPPP requirements can result in significant consequences:
Non-Compliance Consequences
| Type of Consequence | Potential Impact | Examples | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Penalties | Financial | $1,000-$37,500 per day per violation | Based on EPA/state penalty structures |
| Administrative | Permit revocation | May prevent future permit eligibility | |
| Criminal | Jail time for knowing violations | Reserved for severe/willful violations | |
| Project Delays | Schedule | Work stoppage until compliance is achieved | Can extend project timeline by weeks/months |
| Budget | Increased labor and equipment costs | Can significantly impact project profitability | |
| Financing | Potential loan covenant violations | May trigger default provisions | |
| Remediation | On-site | Cleanup of sediment/pollutants | Often more expensive than prevention |
| Off-site | Restoration of damaged resources | May include long-term monitoring requirements | |
| Third-party | Damage to adjacent properties | May result in civil litigation | |
| Reputation | Business | Loss of future contract opportunities | Particularly with public agencies |
| Public | Negative media coverage | Can affect company value/stock price | |
| Industry | Loss of certifications/qualifications | This may impact the ability to bid on specific projects |
- Regulatory Penalties: Fines from state and federal agencies can range from thousands to tens of thousands of dollars per day of violation.
- Project Delays: Stop-work orders issued for non-compliance can set projects back significantly.
- Remediation Costs: Addressing environmental damage caused by inadequate stormwater controls often costs more than implementing proper measures initially.
- Reputation Damage: Non-compliance can harm a company’s standing with regulatory agencies and the public.
How A Better Edge Helps Meet SWPPP Requirements
Our approach to landscape edging naturally complements SWPPP requirements in several ways:
Edging Solutions and SWPPP Compliance
| A Better Edge Product | SWPPP Benefit | Application | Durability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Landscape Edging | Creates clean boundaries between surfaces | Pathways, gardens, planting beds | 20+ years |
| Prevents material migration | Gravel containment, mulch retention | Resistant to rust and corrosion | |
| Defines drainage pathways | Around bioretention areas | Maintains shape through freeze/thaw cycles | |
| Steel Landscape Edging | Strong perimeter definition | Heavy-use areas, commercial projects | 15+ years |
| Erosion prevention at surface transitions | Between hard and soft surfaces | Withstands vehicular traffic | |
| Material containment | Gravel parking areas, pathways | High strength with minimal maintenance | |
| Rubber Landscape Edging | Flexible contouring for curved areas | Natural area transitions | 10+ years |
| Shock-absorbing safety feature | Playgrounds, pedestrian areas | Eco-friendly recycled material | |
| Water channeling | Along drainage swales | Weather-resistant | |
| Concrete Landscape Edging | The permanent division between surfaces | Commercial properties, municipal projects | 25+ years |
| Runoff control | Strategic flow direction | Maximum stability | |
| Superior material containment | Large-scale installations | Low maintenance requirements |
Erosion Prevention
Our aluminum and steel edging products create clear boundaries between different landscape areas, helping contain soil and prevent erosion—a key aspect of SWPPP requirements.
Runoff Control
By properly delineating pervious and impervious surfaces, our edging solutions contribute to managing runoff volumes and velocities by SWPPP requirements.
Long-Term Stability
Unlike temporary measures that must be removed after construction, our permanent edging solutions support erosion control objectives long after completion.
Best Practices for Meeting SWPPP Requirements in Colorado
Based on our extensive experience with Colorado projects, we recommend the following practices to ensure compliance with SWPPP requirements:
Colorado-Specific SWPPP Considerations
| Colorado Factor | Impact on SWPPP | Best Practices |
|---|---|---|
| High-Intensity Summer Storms | Sudden large volumes of runoff | Oversize critical BMPs |
| Implement secondary containment | ||
| Use robust inlet protection. | ||
| Winter Freeze/Thaw Cycles | Frost heave damage to BMPs | Use flexible barriers where possible |
| Inspect frequently during thaw periods. | ||
| Install critical BMPs before the ground freezes. | ||
| High Elevation UV Exposure | Material degradation | Select UV-resistant materials |
| Replace degraded BMPs promptly. | ||
| Provide protective covering where feasible. | ||
| Varying Soil Types | Different erosion potentials | Conduct site-specific soil testing |
| Tailor BMPs to soil characteristics. | ||
| Implement soil amendments where appropriate. | ||
| Steep Topography | Increased erosion potential | Use terracing and slope breaks |
| Implement robust slope stabilization. | ||
| Increase BMP density in steep areas. | ||
| Arid Conditions | Dust control challenges | Implement a comprehensive dust control plan |
| Use water conservation techniques. | ||
| Consider windbreaks for exposed areas. |
- Early Planning: Incorporate stormwater management into the initial design phase rather than treating it as an afterthought.
- Site-Specific Approach: Tailor your SWPPP to the unique characteristics of your site rather than using a one-size-fits-all template.
- Regular Training: Ensure all on-site personnel understand their responsibilities related to SWPPP requirements.
- Documentation: Maintain thorough records of inspections, maintenance activities, and any modifications to control measures.
- Adaptive Management: Be prepared to adjust your approach based on changing conditions and the effectiveness of implemented measures.
Conclusion
SWPPP requirements are vital in protecting Colorado’s water resources from construction-related pollution. Construction projects can minimize environmental impact by implementing practical sediment barriers and stormwater management practices while avoiding costly penalties.
Contact A Better Edge, we understand the challenges of meeting SWPPP requirements while creating beautiful, functional landscapes. Our durable edging solutions enhance your property’s aesthetic appeal and provide long-term environmental protection by supporting effective stormwater management.
Whether planning a small residential project or a significant commercial development, we’re here to help you navigate SWPPP requirements and create sustainable, compliant landscapes that stand the test of time. Contact us today to learn more about how our landscape edging solutions can support your stormwater management goals.
More information is available on the Colorado Department of Public Health & Environment website: COR400000 Construction Stormwater Discharge Permit.